Application of 3D Cell Explorer to Histology and Histopathology
Cancer Detection
On this page you can explore cancer detection as we see it: in 3‐D and stain‐free.
The 3D Cell Explorer allows for:
- Detection of cancer cells based on morphological markers and refractive index (“RI”) markers;
- Better 3‐D visualization of tumor in tissue slides.
Histopathology of a patient’s biopsy has always been the most useful tool for detecting or confirming the presence of cancerous tissues. This is why patients usually have their cancer diagnosis confirmed on tissue pathology. Histopathologists interpret those diseased tissues under a microscope to make a diagnosis.
However, the preparation of these samples can be tedious, expensive and time‐consuming. In order to view the tissue, the sections must be stained to create contrast.
The 3D Cell Explorer offers a way to avoid this process. Based on the physical properties of the cells (the Refractive Index of the different components), a post‐acquisition digital staining of the sample can be performed, meaning that no pre‐observation is required.
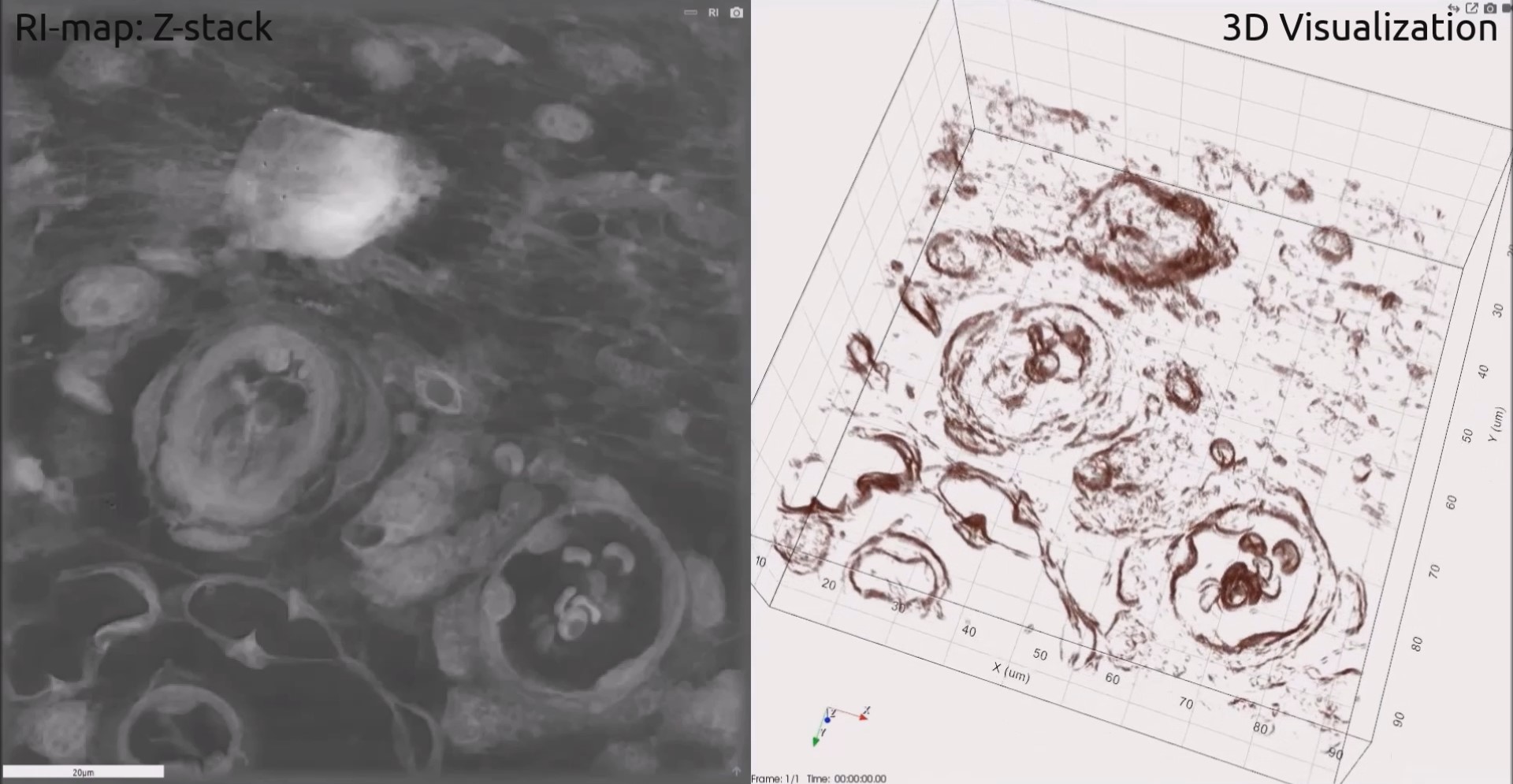
Slice of xenograft of human breast cancer in mouse. Cell line: MDA-mb-231 (part 1)
The mouse tumor was excised from the sacrificed animal, fixed in 4% PFA in PBS and embedded in OCT. The organ was then sectioned (8µm) in a cryostat and mounted on glass slides.
Slice of xenograft of human breast cancer in mouse. Cell line: MDA-mb-231 (part 2)
The mouse tumor was excised from the sacrificed animal, fixed in 4% PFA in PBS and embedded in OCT. The organ was then sectioned (8µm) in a cryostat and mounted on glass slides.
Tissue Morphological Analysis and 3‐D Characterization
On this page you can explore tissue morphology as we see it: in 3‐D and stain‐free.
The 3D Cell Explorer allows for:
- Label‐free, 3D tissue visualizations (thickness up to 20 micrometers);
- 3D Localization of ROI inside the tissue slide, based on its specific refractive index (“RI”).
Tissue morphological analysis is usually done on a sick patient’s biopsy. Thanks to the visualization of the tissue slide, the trained pathologist is able to give a diagnosis on the health of the patient. The usual approach for analyzing such slides is chemical staining which gives contrast to the transparent structures. The most common method is the Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining.
However, this procedure requires a lot of reagents and time.
Nanolive’s technology bypasses these limitations thanks to the digital staining of the slide, and you can now avoid all this preparation. Based on the structures’ physical properties (Refractive Index), the 3D Cell Explorer is able to replace the chemical staining with a digital one.
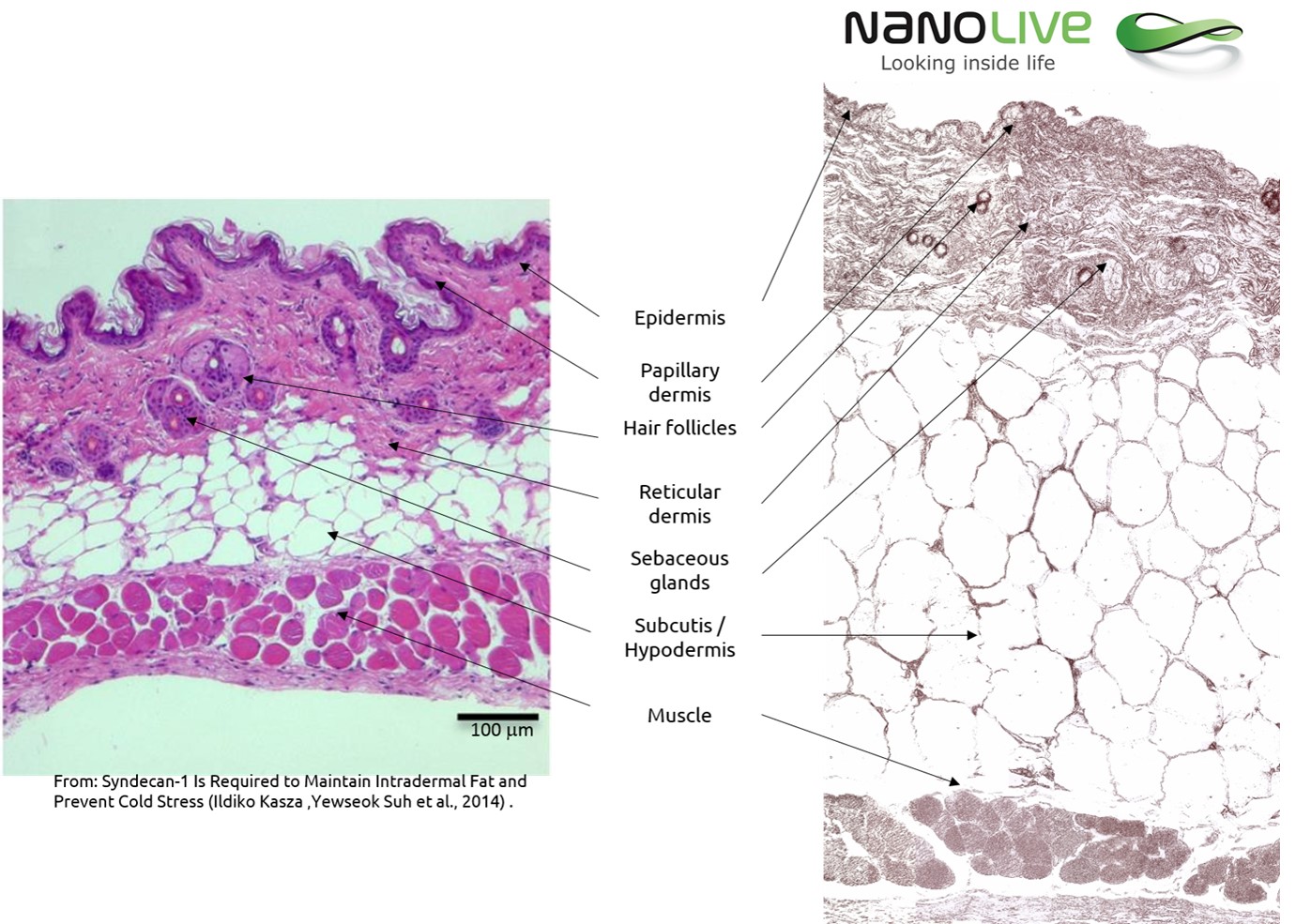
Mouse Skin Section Observation with the 3D Cell Explorer
Paraffin‐fixed Mouse skin sections of 8 µm. They were then dried overnight at 37°C before being dewaxed and rehydrated. Then they were rehydrated again, cleared in xylene and mounted in a xylene‐based glue.
Portal Triad in Mouse Liver
Paraffin‐fixed mouse kidney section of 8 µm. They were then dried overnight at 37°C before being dewaxed and rehydrated. Then they were rehydrated again, cleared in xylene and mounted in a xylene‐based glue.
Tissue Section of Mouse Myocardium
Paraffin‐fixed mouse myocardium section of 8 µm. They were then dried overnight at 37°C before being dewaxed and rehydrated. Then they were rehydrated again, cleared in xylene and mounted in a xylene‐based glue.
Tissue Section of Mouse Intestine
Paraffin‐fixed mouse trachea section of 8 µm. They were then dried overnight at 37°C before being dewaxed and rehydrated. Then they were rehydrated again, cleared in xylene and mounted in a xylene‐based glue.
Tissue Section of Mouse Pancreas
Paraffin‐fixed mouse pancreas section of 8 µm. They were then dried overnight at 37°C before being dewaxed and rehydrated. Then they were rehydrated again, cleared in xylene and mounted in a xylene‐based glue.
Tissue Section of Mouse Kidney
Paraffin‐fixed mouse kidney section of 8 µm. They were then dried overnight at 37°C before being dewaxed and rehydrated. Then they were rehydrated again, cleared in xylene and mounted in a xylene‐based glue.
Tissue Section of Mouse Trachea
Paraffin‐fixed mouse trachea section of 8 µm. They were then dried overnight at 37°C before being dewaxed and rehydrated. Then they were rehydrated again, cleared in xylene and mounted in a xylene‐based glue.